- Related Questions & Answers
- Selected Reading
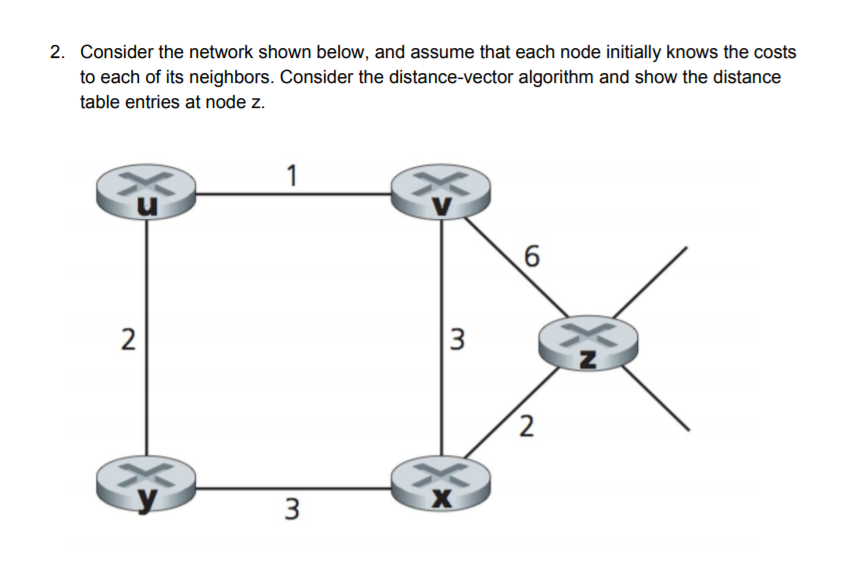
- F Enter the router whose routing table is to be found out: C Enter the no of routers adjacent to this router: 3 Enter the distances of each router from this router: ROUTER DISTANCE - - A 11 B 6 C 0 D 3 E 5 F 6 Enter the name of the adjacent router 1: B Enter the distances of each router from this router: ROUTER DISTANCE.
- I want to develop Distance Vector routing Algorithm based on java programming language, I am using Netbeans Software to do it. If any body could give me advice or links where I can get help. Posted 7-Dec-14 22:33pm.
- Distance Vector Routing Algorithm Page 5. 5 The shortest path from 1 to 5 is 1-4-5 Minimum Cost = 3 End of Distance Vector program. The code uses some of the functionality which is present in Java 1.5.
The Distance-Vector routing algorithm is known by other names. Bellman-Ford routing algorithm and the Ford-Fulkerson algorithm are generally distributed after the researchers create it (Bellman 1957, and Ford and Fulkerson, 1962).
Features
8086 Assembly Program to Find Smallest Number from Given Numbers; 8086 Assembly Program for Addition of Two 8 bit Numbers; 8086 Assembly Program to Convert Binary Number into BCD Format; 8086 Assembly Program for Division of Two 8 bit Numbers; Discussions. Tefera on Implementing Diffie–Hellman Key Exchange Algorithm in Java. This assignment has two parts. The first part consists of four tasks: design, implementation, test and demonstration of a program in Java that implements a distributed and asynchronous distance vector routing protocol, based on the Bellman-Ford equation.
Following are the features of the distance vector routing are −
The routers send the knowledge of the whole autonomous framework.
Sharing of data takes place only with the neighbours.
Sending of data holds place at constant, ordinary intervals, declared every 30 seconds.
In this algorithm, each router evaluates the distance between itself and every achievable destination. This is accomplished by assessing the distance between a router and all of its immediate router neighbours and adding each neighbouring routers computations for the distance between that neighbour and its close neighbours.
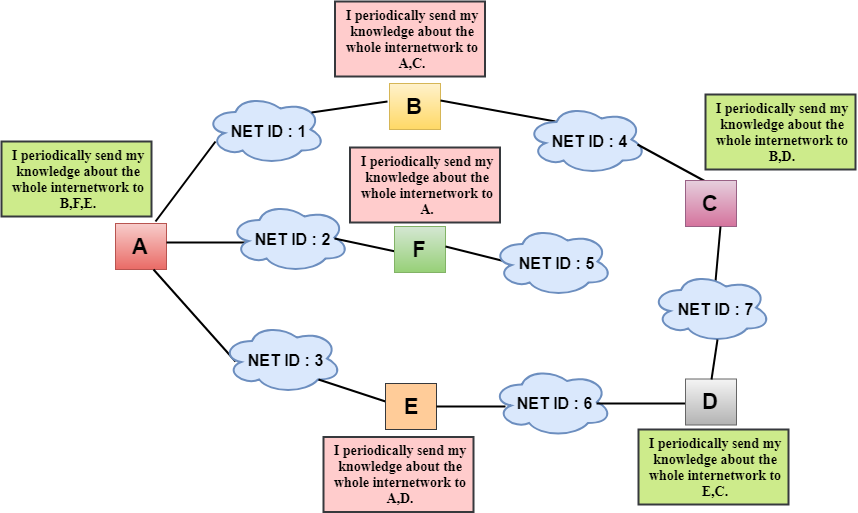
Three keys to learn how this algorithm works are as follows −
Knowledge about the entire network

Each router sends its knowledge about the entire network. It communicates all of its connected knowledge about the network to its neighbours.
Routing only to the neighbours
Each route repeatedly shares its knowledge about the network only to those routers with the explicit connection. It transmits whatever knowledge it has about the complete network by all of its parts. This data is taken and stored by each neighbouring router and can upgrade the routers own data about the network.
Information sharing at regular intervals
In distance vector routing, each router repeatedly sends its knowledge about the whole network with its neighbours. For example, after 30 seconds, each router shares its data about its neighbour's entire network.
In this, the rectangular box represents LANs. The number inside each rectangular box is the LANs Network ID. These LANs are linked by a router, described by the boxes such as A, B, C, D, E. The square boxes denote the connection of the routers to their neighbours.
Routing table creation and updating
This table has three columns which contain the information about network id, cost & Next Hop. Let the original tables for each router be.

For router A
Distance Vector Routing Algorithm Program In Java
| Network id | Cost | Next Hop |
|---|---|---|
| 24 | 1 | B |
| 23 | 1 | E |
| 88 | 1 | F |
For router B
| Network id | Cost | Next Hop |
|---|---|---|
| 24 | 1 | A |
| 65 | 1 | C |
For router E
| Network id | Cost | Next Hop |
|---|---|---|
| 23 | 1 | A |
| 18 | 1 | D |
For router D
| Network id | Cost | Next Hop |
|---|---|---|
| 18 | 1 | E |
| 76 | 1 | C |
When A can send his packet or routing table information to B router, E & C directly.
Similarly, B can send routing table information to router A & C and so on.
Distance Vector Routing Algorithm Program In Javascript
When A receivers are routing tables from B, E & F, it can update its table. Similarly, B receives A and C updates itself and so on, as shown in the new table.
Distance Vector Routing Algorithm Program In Java Free
New routing table for router A
| Network id | Cost | Next Hop |
|---|---|---|
| 23 | 1 | E |
| 24 | 1 | B |
| 88 | 1 | F |
| 23 | 2 | D |
| 38 | 2 | C |
New routing table for router B
Distance Vector Routing Algorithm Program In Java Pdf
| Network id | Cost | Next Hop |
|---|---|---|
| 13 | 2 | A |
| 24 | 1 | A |
| 28 | 1 | C |
| 35 | 2 | C |
| 38 | 2 | C |
Similarly, every router will update itself and so on. The updating algorithm checks that the router first adds Hop to the Hop count field for each advertised route. The router should apply these rules.
If the displayed destination is not in the routing table, the router must insert that displayed data into the table.
If the displayed destination is in the routing table, then two things can happen.
Distance Vector Routing Algorithm Program In Java Download
If the next-hop field is similar, the router must restore the table's entry with the displayed one.
Distance Vector Routing Algorithm Program In Java Pdf
If the next-hop field is not a similar
Distance Vector Routing Algorithm Program In Java Tutorial
If the displayed hop count is lesser than the one on the table, the router must restore the entry in the table with the new one.
If the displayed hop count is not lesser, the router must do nothing.



